執行計畫
Mechanistic study of cholesterol deficiency aggravating glutamate-induced cytoxicity
Mechanistic study of cholesterol deficiency modulating cell viability
Representative Papers
-
- Tsai, H.-I, Tsai, L.-H., Chen, M.-Y.and Chou, Y.-C. (2006) Cholesterol deficiency perturbs actin signaling and glutamate homeostasis in hippocampal astrocytes. Brain Res. 1104:27-38.
- Chou, Y.-C., Yu, S., and Lin, S.B. (1999) Cholesterol depletion exacerbates glutamate-induced cell death in hippocampal cultures. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 23:1142.
- Huang, Z.-H, Wu, H.-J., Yeh, C.-C., Chou ,Y.-C. and Chang, Y.-C. (2006) Dendritic spines of developing rat cortical neurons in culture. Chinese J. Physiol. 49:1-7.
- Chou, Y.-C., Lin, S.-B, Tsai, l.H., Tsai, H.-I., and Lin, C.M. (2003) Cholesterol deficiency increases the vulnerability of hippocampal glia in primary culture to glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Neurochem. Intl. 43:197-209.
- Lin, Y.-C., Huang, Z.-H., Jan, I.-S., Yeh, C.-C., Wu, H.-J., Chou, Y.-C., and Chang, Y.-C. (2002) Development of excitatory synapses in cultured neurons dissociated from the cortices of rat embryos and rat pups at birth. J. Neurosci. Res. 67:484-493.
- Chiang, A.-N., Chang, C.-P., Chou, Y.-C., Huang, K.-Y., and Hu, H.-H. (1999) Differential distribution of apolipoprotein E in young and aged spontaneously hypertensive and stroke-prone rats. J. Hypertension 17:793-800.
- Chou, Y.-C. (1998) Corticosterone exacerbates cyanide-induced cell death in hippocampal cultures: role of astrocytes. Neurochem. Intl. 32:219-226.
Research Interest
諸多研究結果証實,腦部疾病所見之細胞死亡係因腦細胞釋出過多之麩胺酸 (glutamate) 所致。這些麩胺酸一經釋出之後,便與其受體結合,由於受體之過度活化,因而造成大量鈣離子積聚於細胞內,最後導致神經細胞死亡。由於腦部海馬迴 (hippocampus) 組織主司學習與記憶,對於麩胺酸所致之細胞毒殺作用又甚為敏感,因此我們便以初級海馬迴細胞培養 (primary cultures of hippocampal cells) 做為模式系統,探討麩胺酸引致海馬迴細胞死亡的機轉及其調控作用
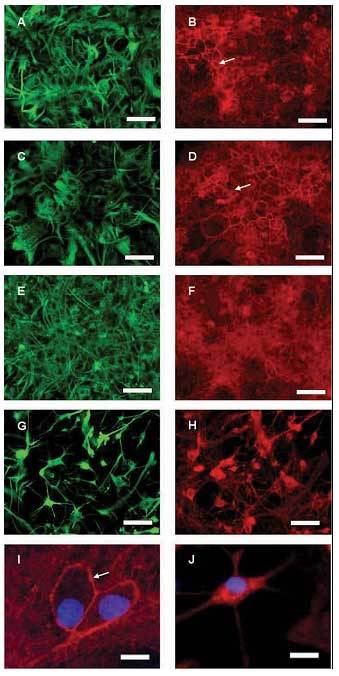
我們先前之研究證實膽固醇不足會加劇麩胺酸對於海馬迴星狀神經膠細胞之毒殺作用,然而此一作用並不見於神經細胞。針對此一現象,我們進而探討膽固醇短缺對於海馬迴細胞之影響,我們發現膽固醇短缺導致星狀神經膠細胞內cortical actin ring 瓦解 (圖一)、刺激 extracellular-signal regulated kinase (ERK) 之磷酸化 (圖二) 及麩胺酸運送子 (glutamate transporter) 之活性,並抑制glutamine synthetase (GS) 之表現與酵素活性 (圖二),但是膽固醇短缺之神經細胞,其 actin細胞骨骼 (cytoskeleton) 結構以及 ERK磷酸化未見任何異常。由於星狀神經膠細胞因膽固醇不足所衍生之變異亦見於阿滋海默氏症患者腦部之星狀神經膠細胞,因此我們將進一步探討膽固醇短缺調控 actin、ERK之訊息傳導及麩胺酸恆定作用之機轉,希冀有助於吾人對於膽固醇調控腦細胞功能之瞭解,同時亦有助於腦部疾病如阿滋海默氏症之治療。
膽固醇短缺導致海馬迴星狀神經膠細胞內cortical actin ring 瓦解。星狀神經膠細胞經 lovastatin及b-cyclodextrin移除細胞膽固醇之處理 0 (A, B, I)、24 (C, D)、48 (E, F)或72 (G, H, J) 小時之後,再以辨識星狀神經膠細胞之GFAP抗體 (綠色)及辨識 actin 之phalloidin (紅色)進行染色,同時又以 DAPI 標定細胞核 (藍色)。箭頭所指即為 cortical actin ring。
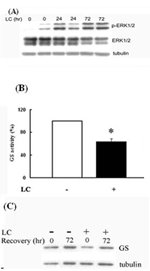 膽固醇短缺刺激 extracellular-signal regulated kinase (ERK)之磷酸化,並抑制 glutamine synthetase (GS)之表現與酵素活性。(A)星狀神經膠細胞經 lovastatin及b-cyclodextrin之處理 0、24或72小時之後,再以西方點墨法 (Western blotting) 分析ERK之表現及ERK之磷酸化。(B)星狀神經膠細胞經 lovastatin及b-cyclodextrin處理 0 (-)或72 (+)小時之後,再分別量測細胞之 GS 活性。(C)星狀神經膠細胞經 lovastatin及b-cyclodextrin處理 0 (-)或72 (+)小時之後,再予以原先之細胞培養基處理 0 或 72小時,再以西方點墨法分析GS之表現。
膽固醇短缺刺激 extracellular-signal regulated kinase (ERK)之磷酸化,並抑制 glutamine synthetase (GS)之表現與酵素活性。(A)星狀神經膠細胞經 lovastatin及b-cyclodextrin之處理 0、24或72小時之後,再以西方點墨法 (Western blotting) 分析ERK之表現及ERK之磷酸化。(B)星狀神經膠細胞經 lovastatin及b-cyclodextrin處理 0 (-)或72 (+)小時之後,再分別量測細胞之 GS 活性。(C)星狀神經膠細胞經 lovastatin及b-cyclodextrin處理 0 (-)或72 (+)小時之後,再予以原先之細胞培養基處理 0 或 72小時,再以西方點墨法分析GS之表現。

從分子到認知的整合型神經科學研究
教學及研究本著希望啟發及培育下一代神經科學人才,
將來對了解人類心理狀態、行為的根源及治療神經系統
的疾病有所貢獻。

